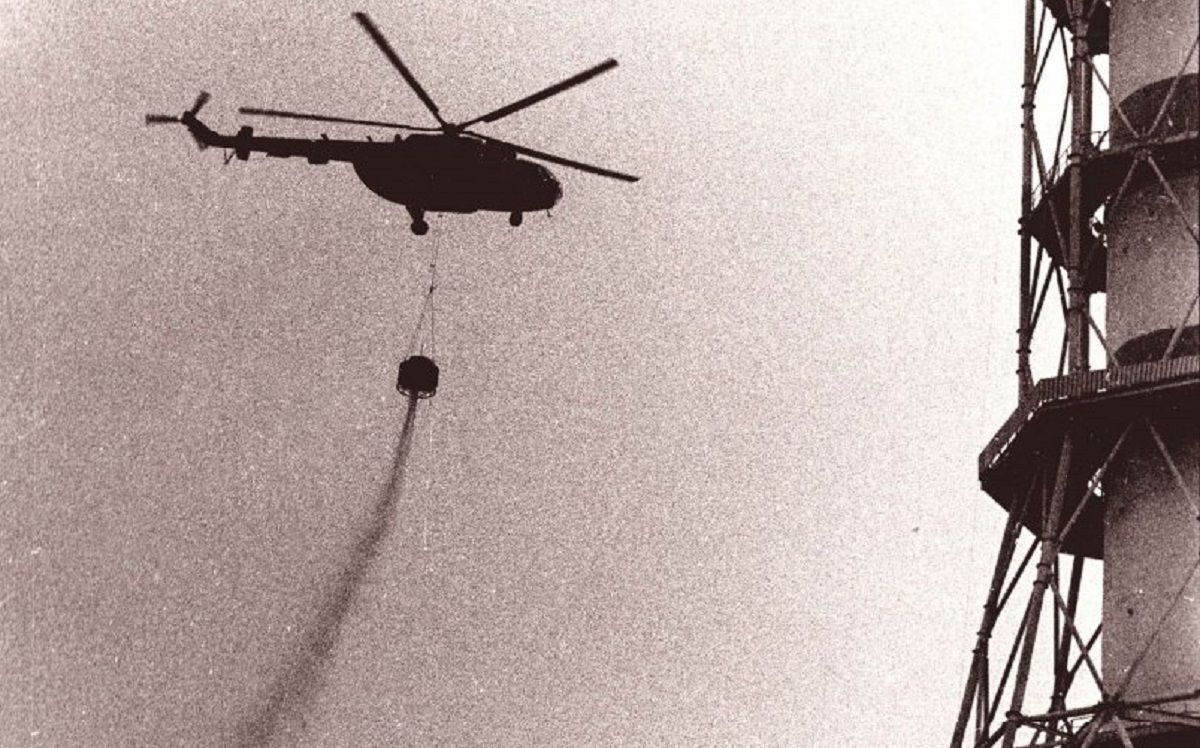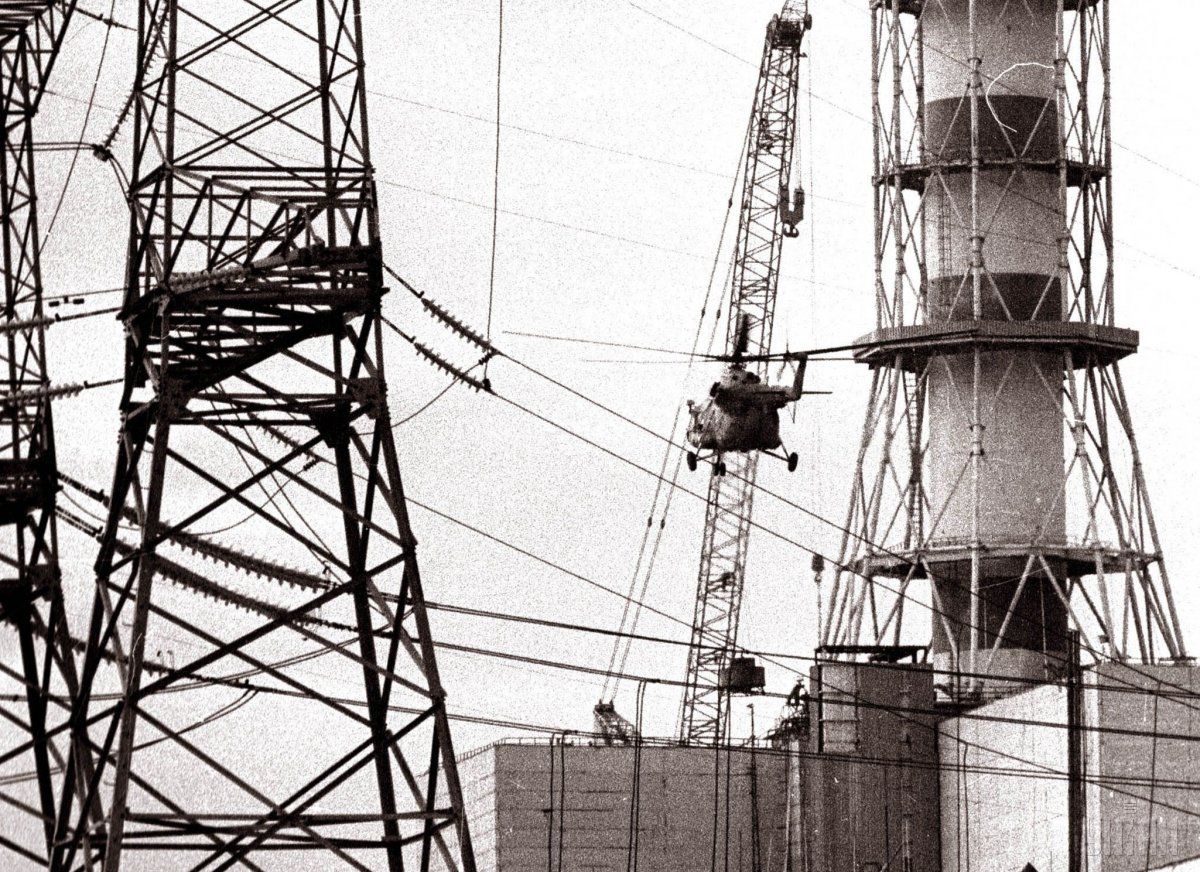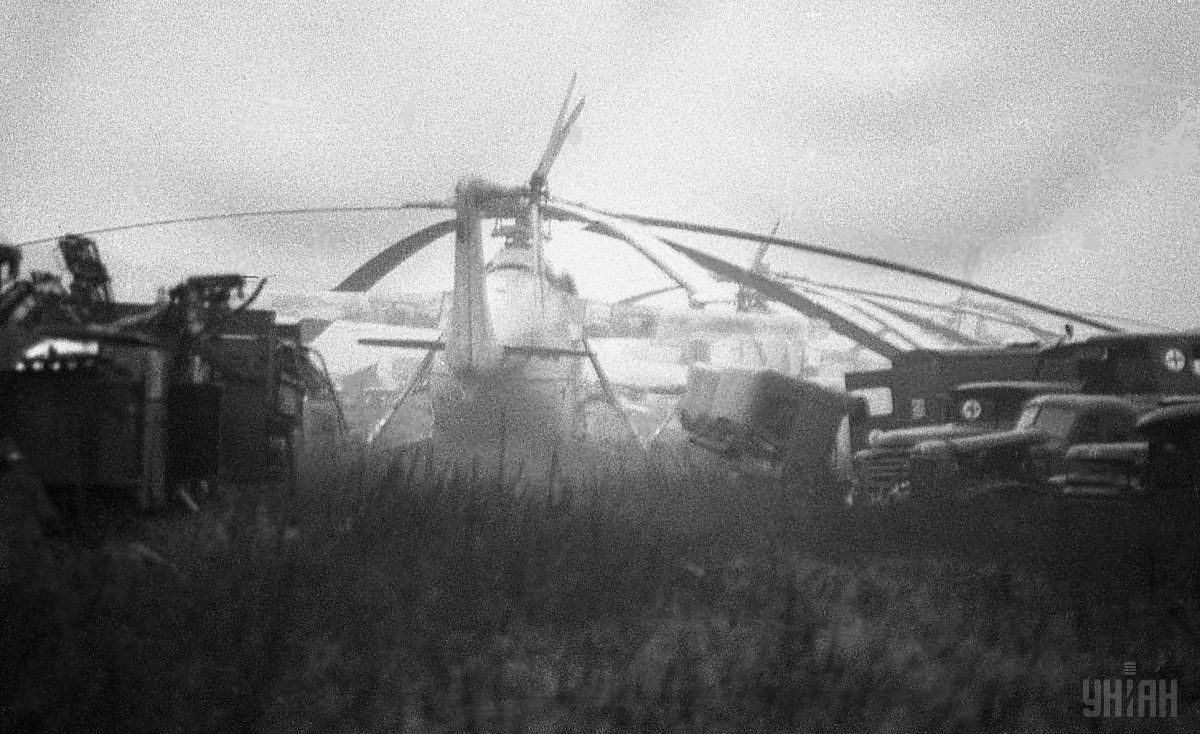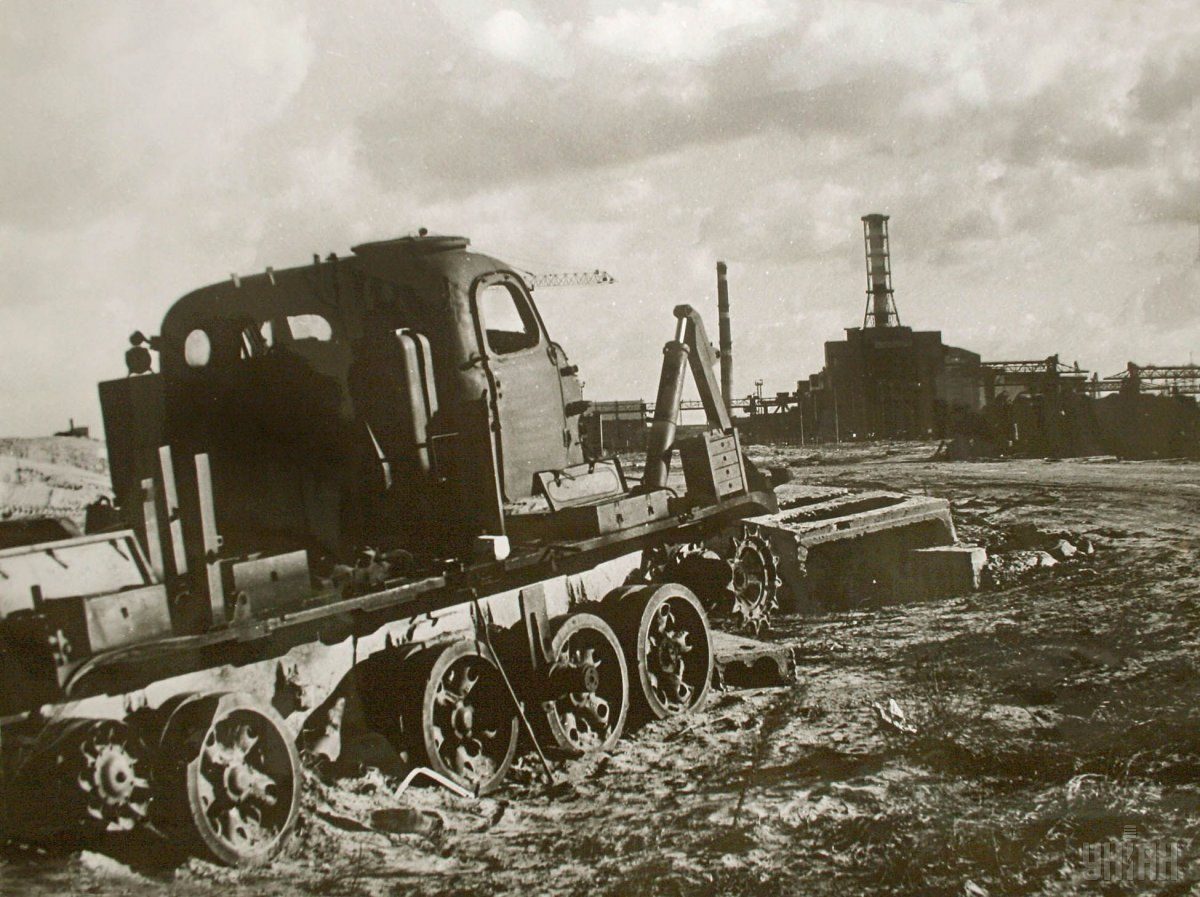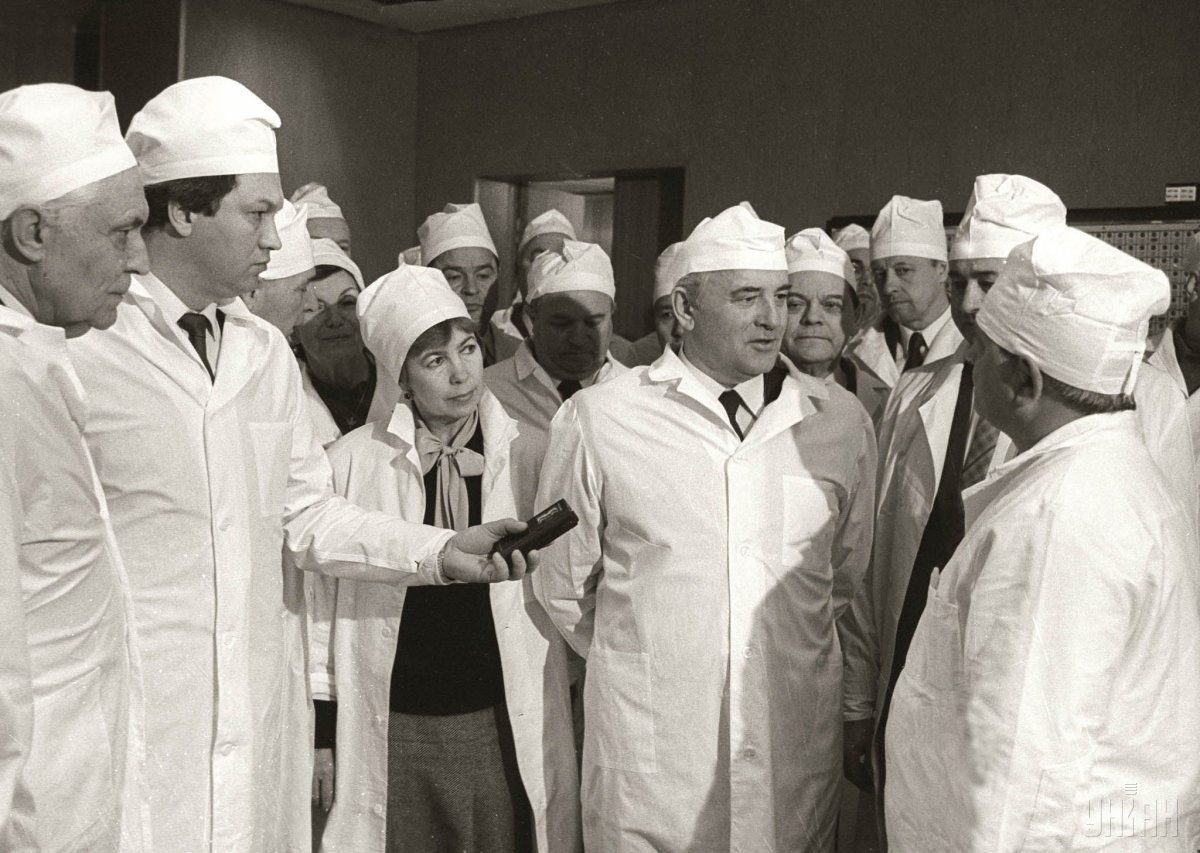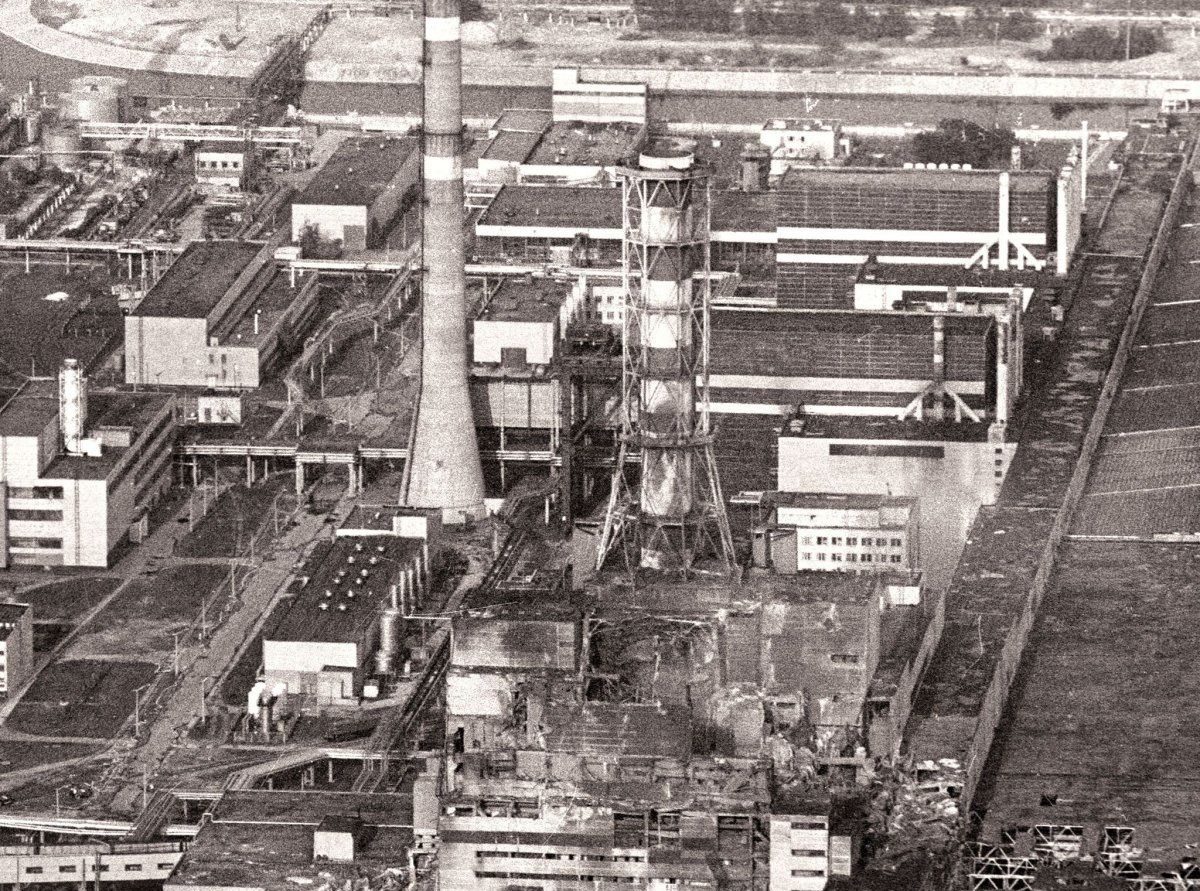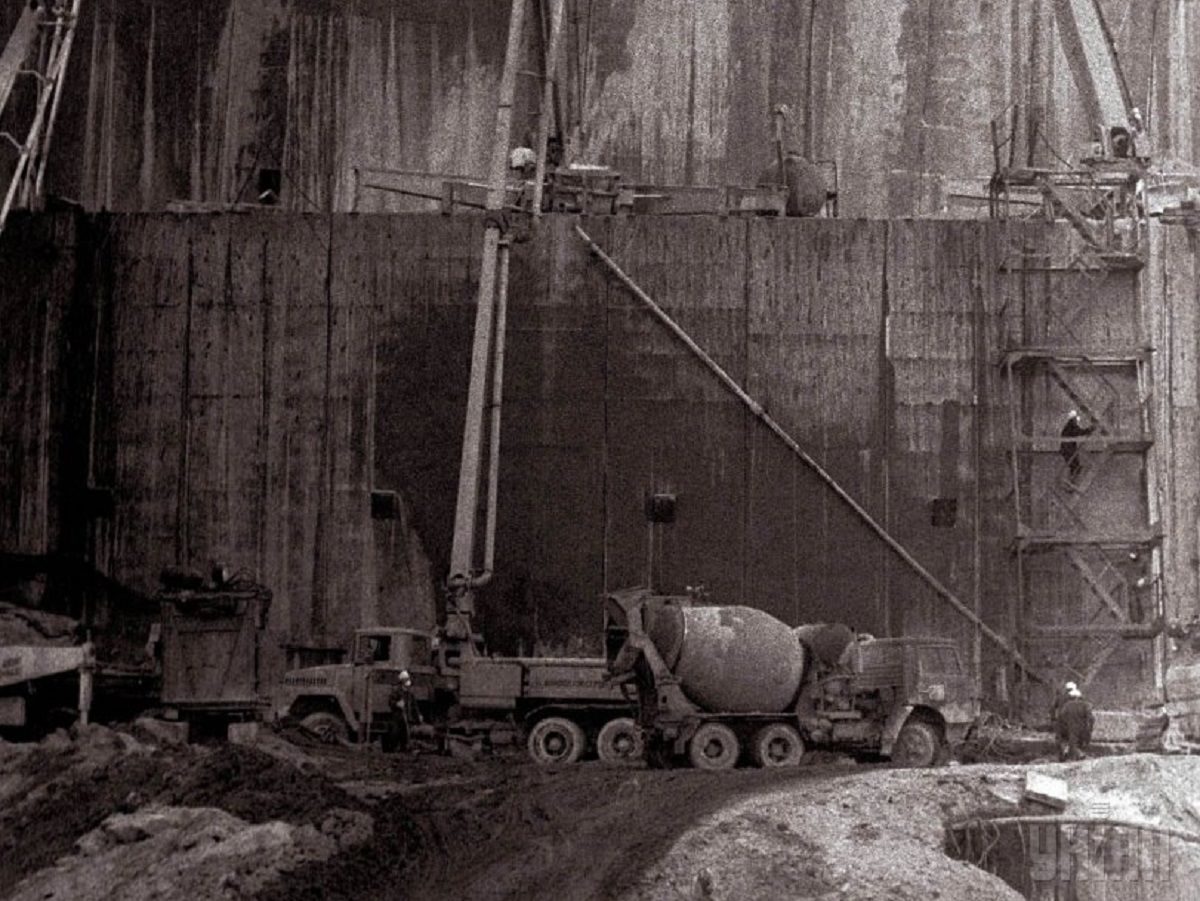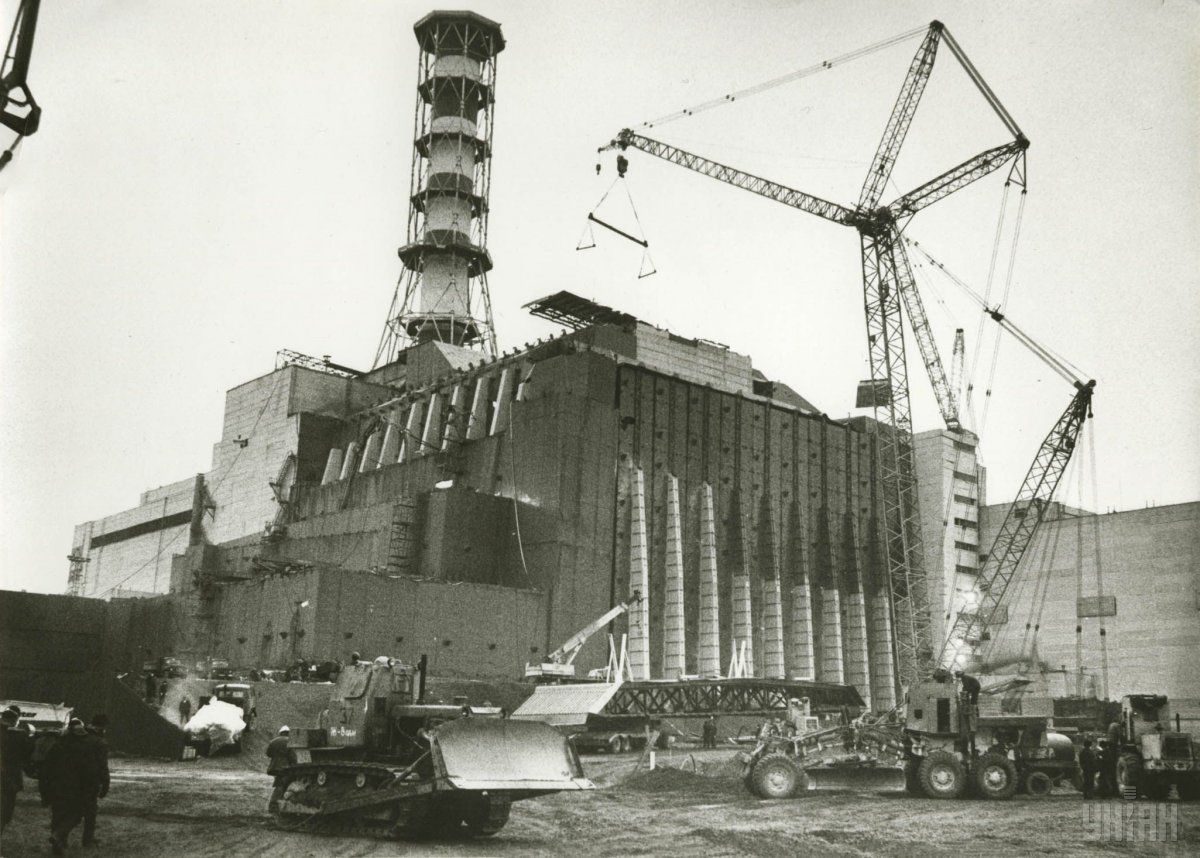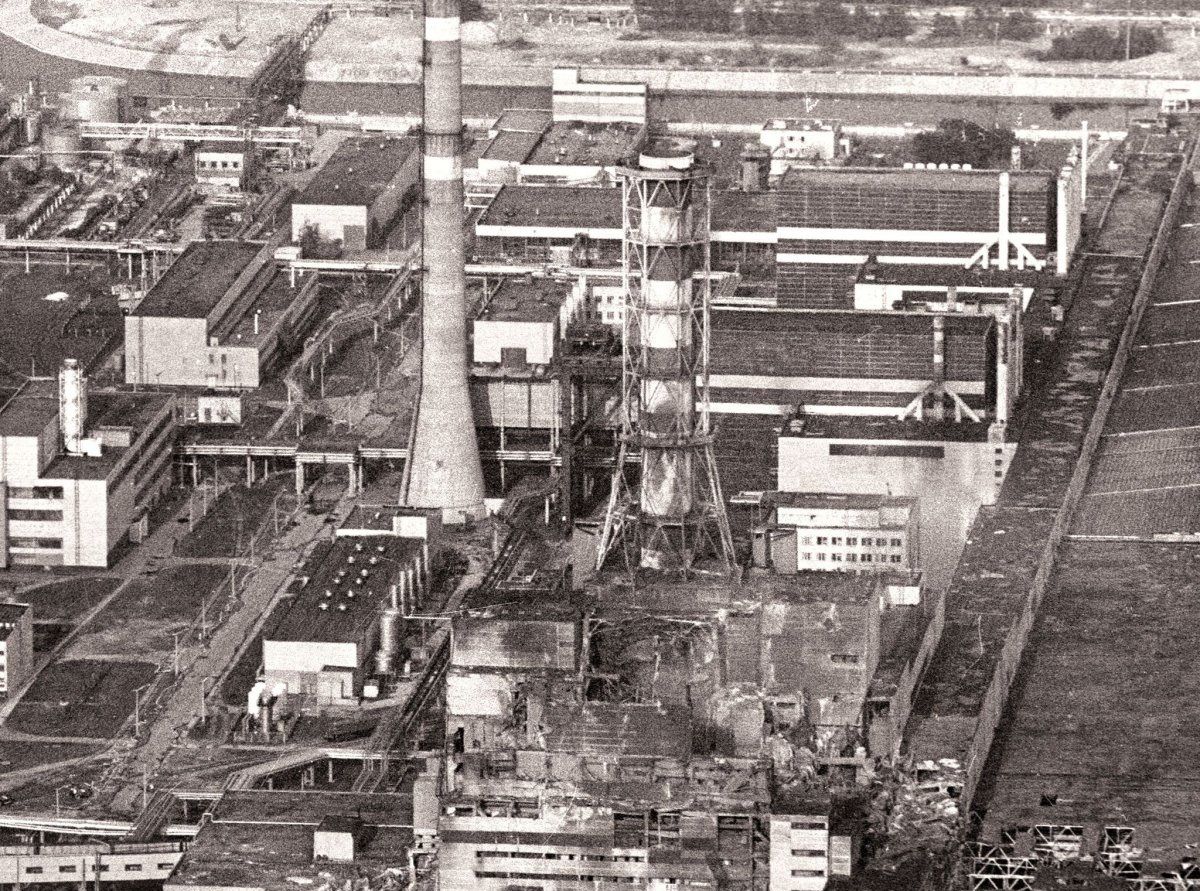
According to archive data, at 01:23 on April 26, 1986, a reactor at power unit 4 of the Chornobyl NPP was completely destroyed in a series of thermal explosions. A significant amount of radioactive substances was released into the environment. The accident is regarded as the largest of its kind in the history of nuclear energy, both in terms of victims and the economic losses.
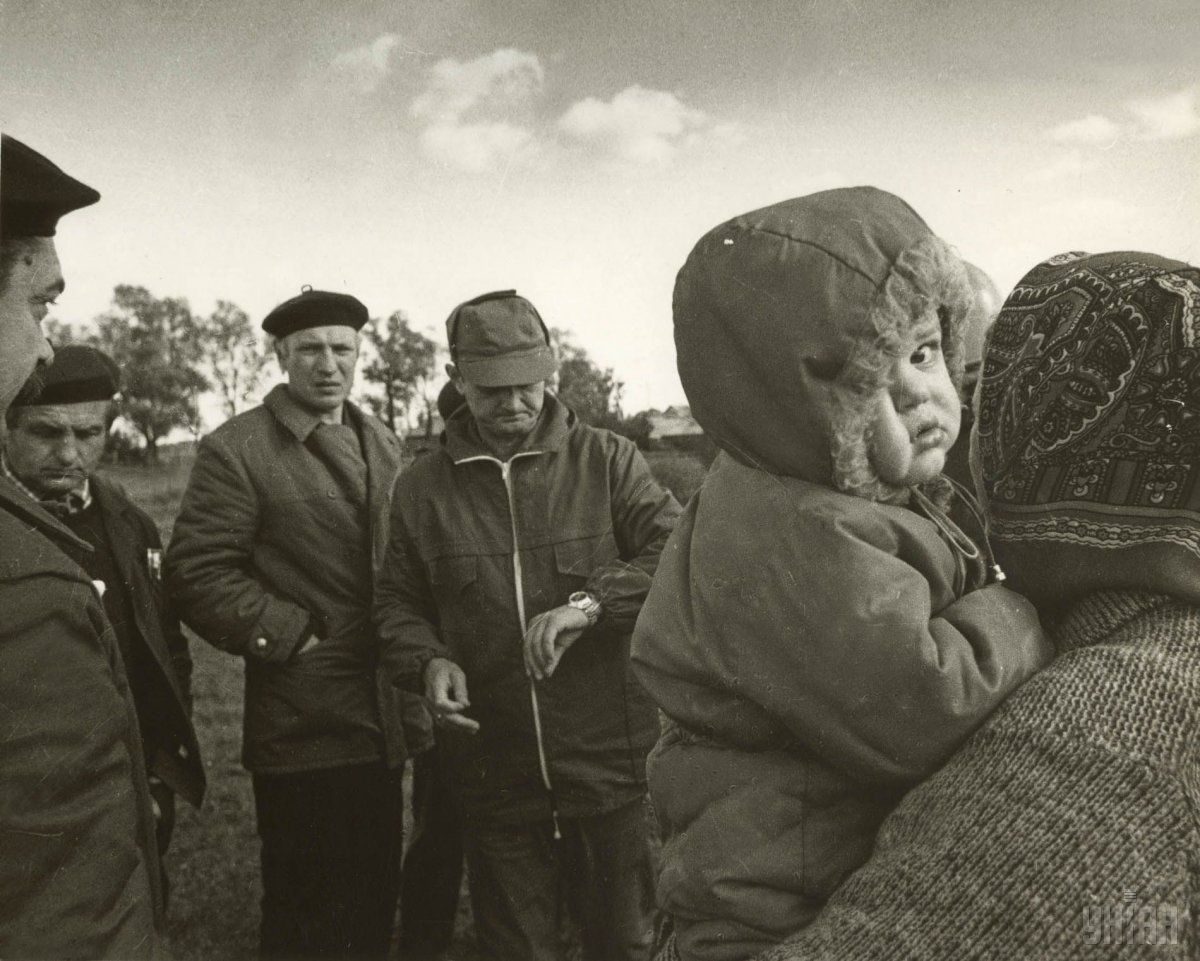
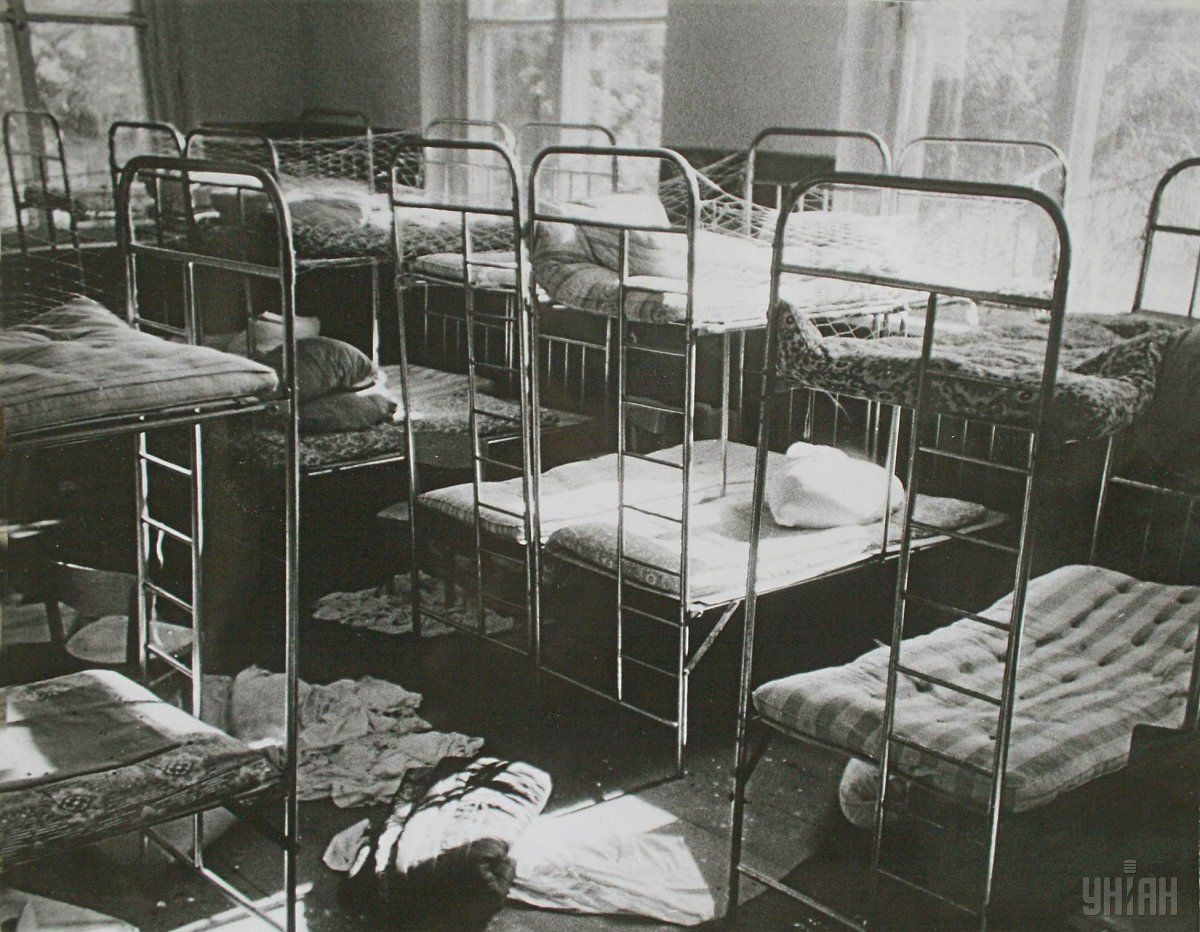
After the Chornobyl disaster, 116,000 people were evacuated from the affected areas, while another 230,000 people were resettled from the contaminated area. A total of 167,653 victims died, including 2,929 liquidators. 83% of victims, including 92% of the emergency response team, are suffering from various diseases.
As of today, the causes of the accident are identified as such: the reactor was improperly designed and dangerous; the staff was not informed of the threats; the staff made a number of mistakes and deliberately violated the existing regulations, partly due to the lack of information about the dangers of the reactor; the protection tripping had no impact on the development of the accident or did not contradict the regulations.
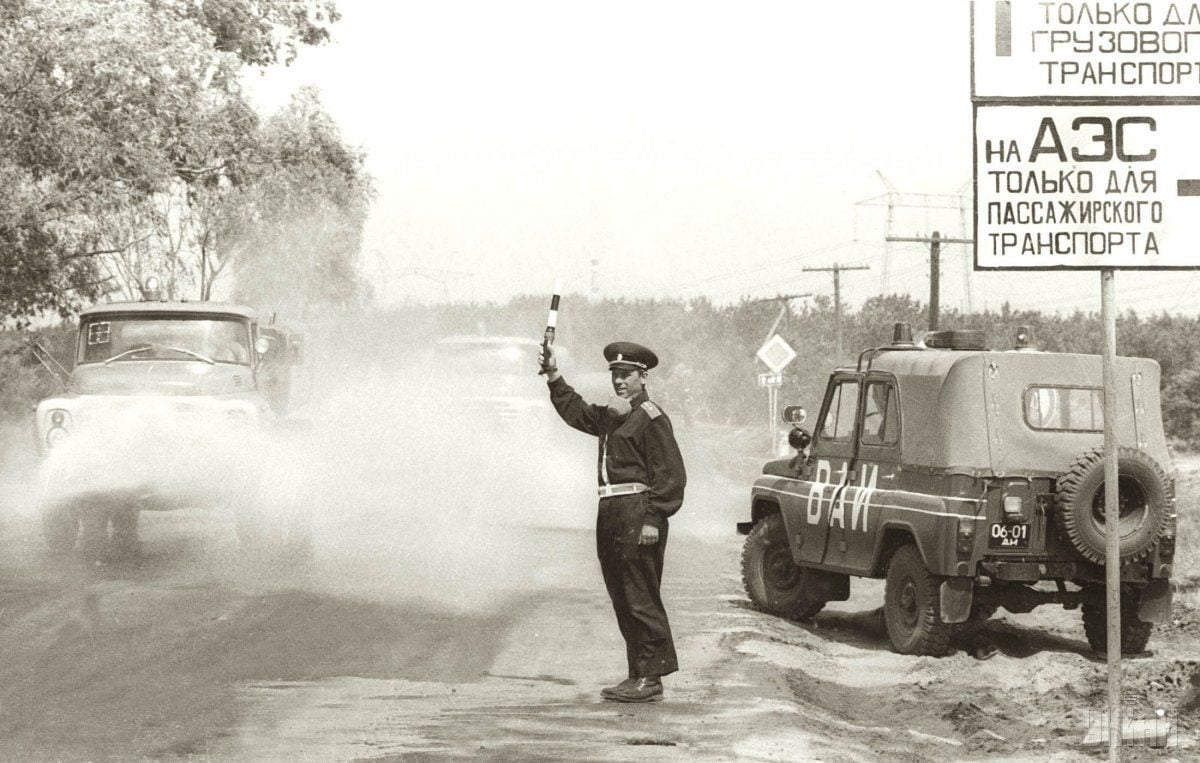
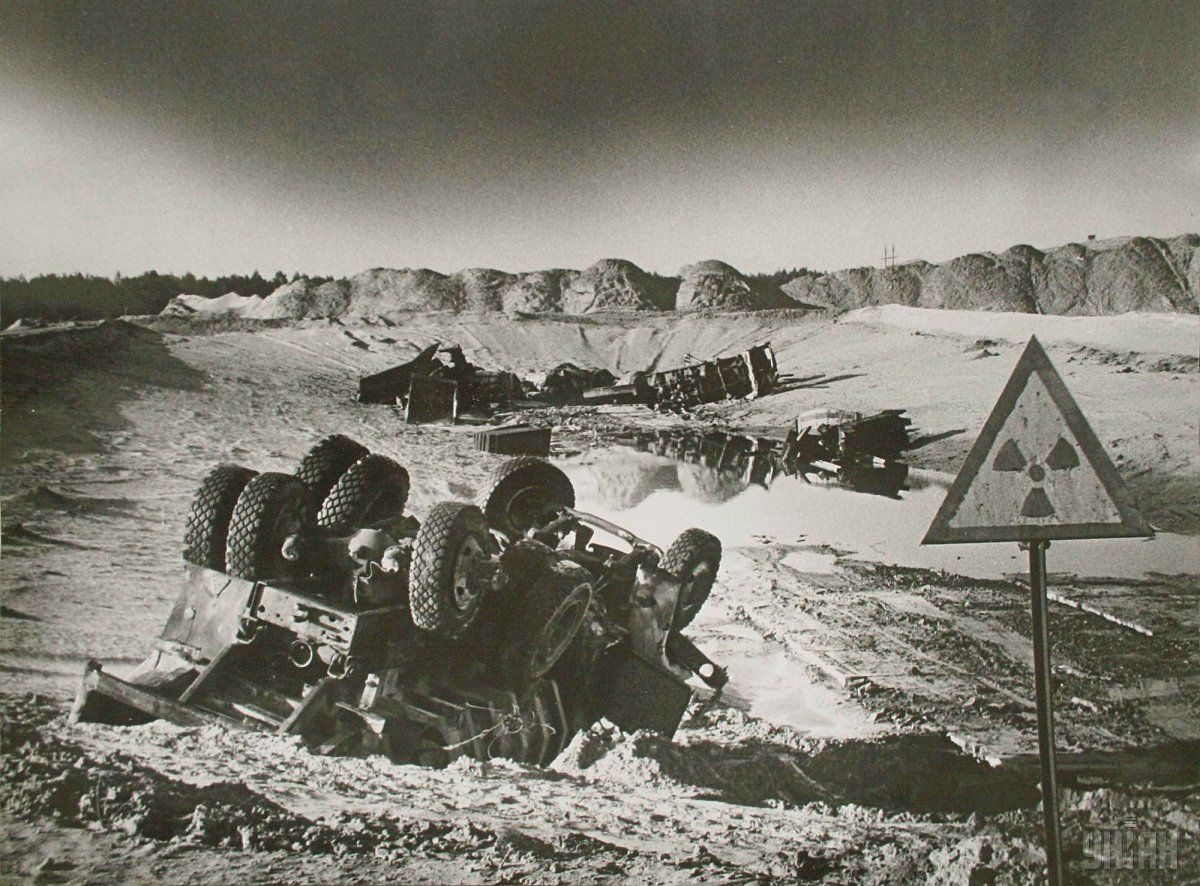
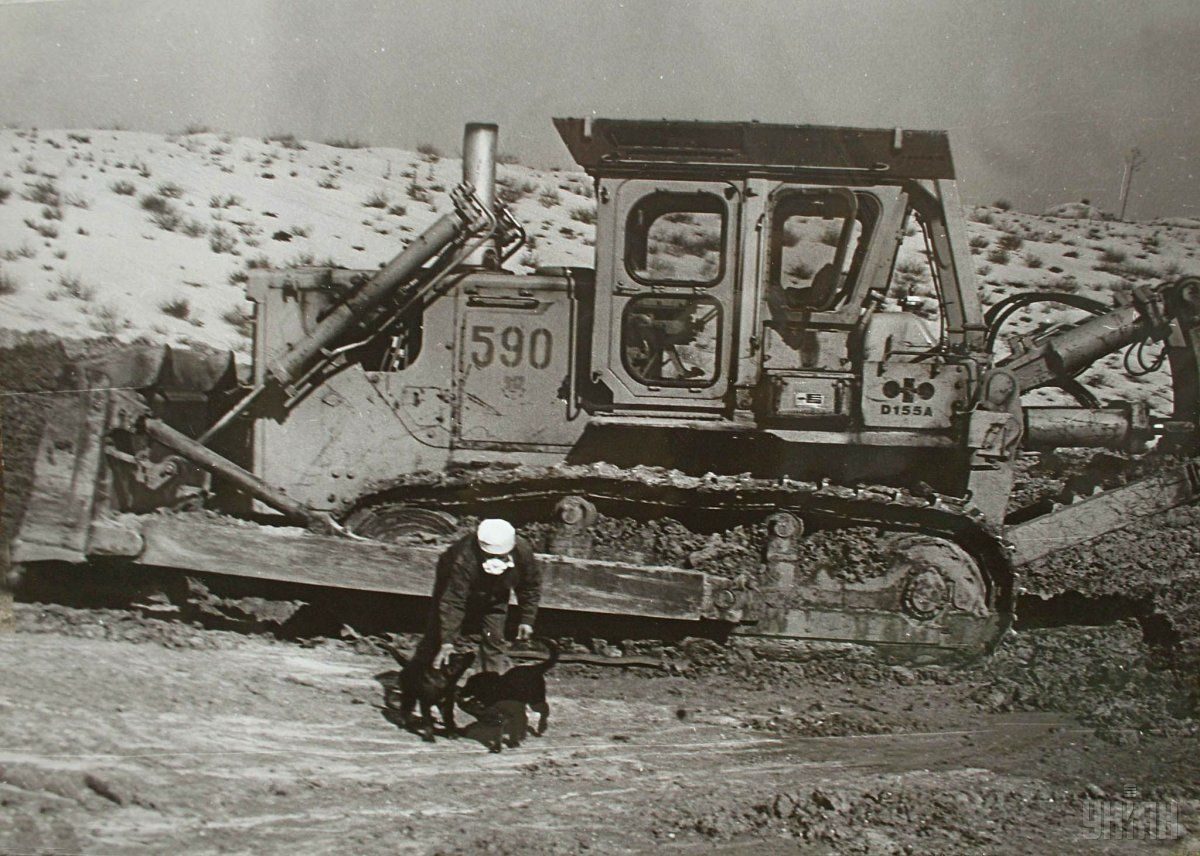
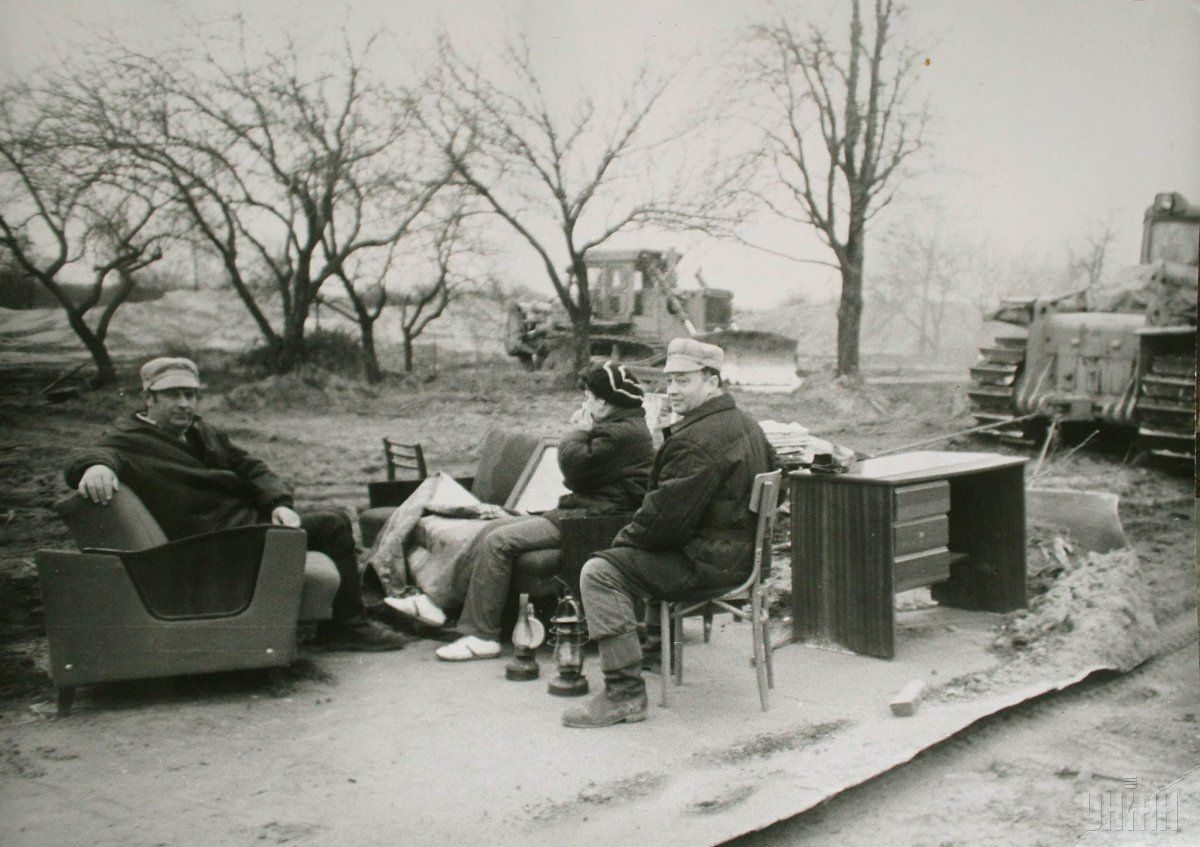
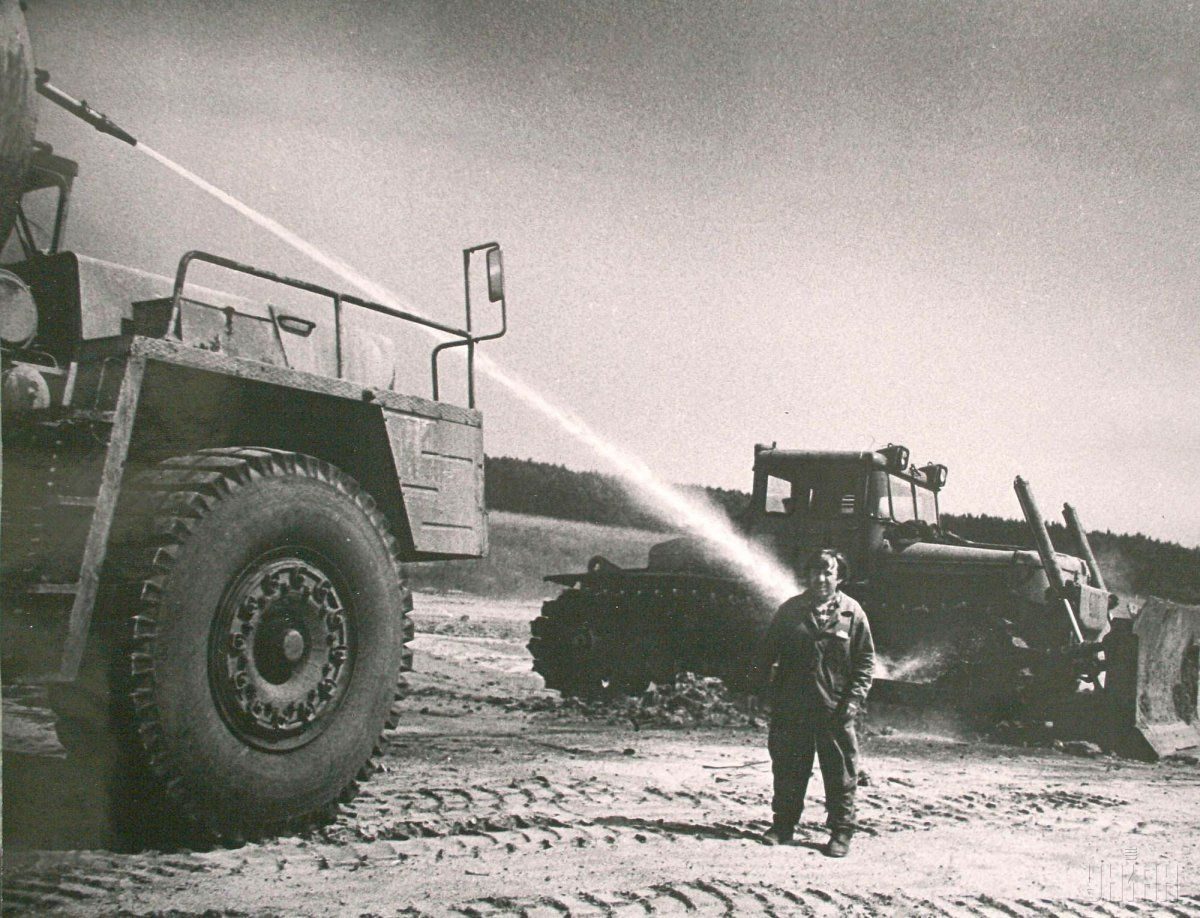
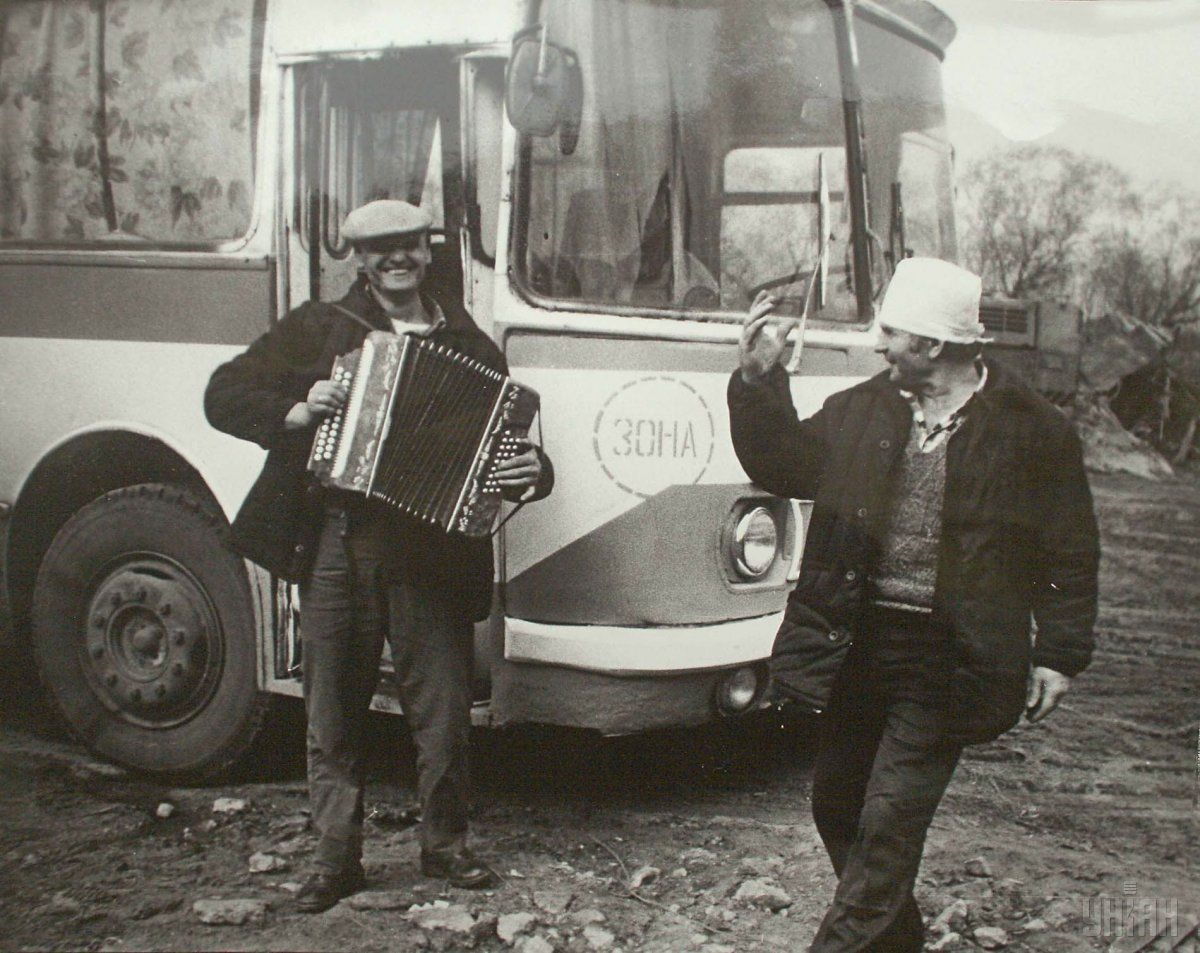
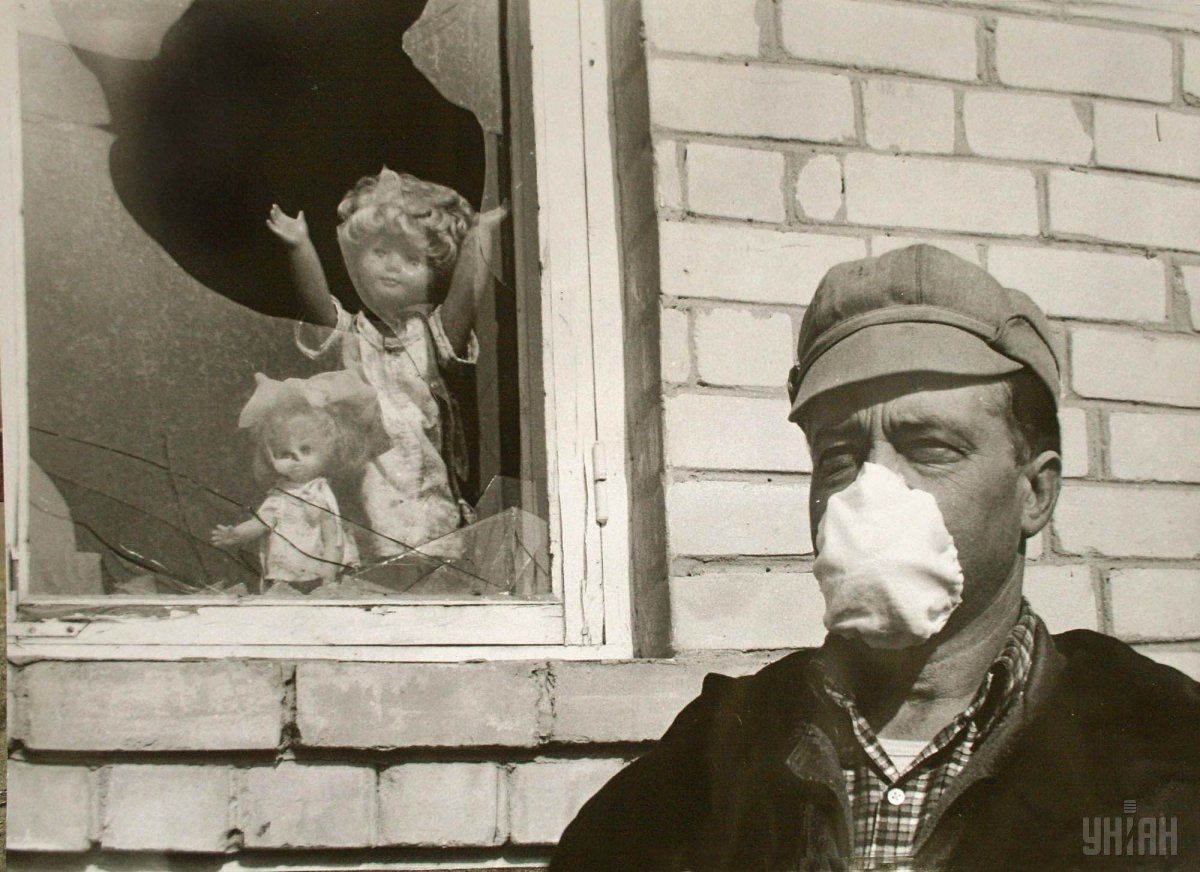
At the moment, the so-called exclusion zone of 30 kilometers around the plant, established in 1986 after the evacuation of the population, is a no-go territory. This area has suffered intense pollution by radionuclides.
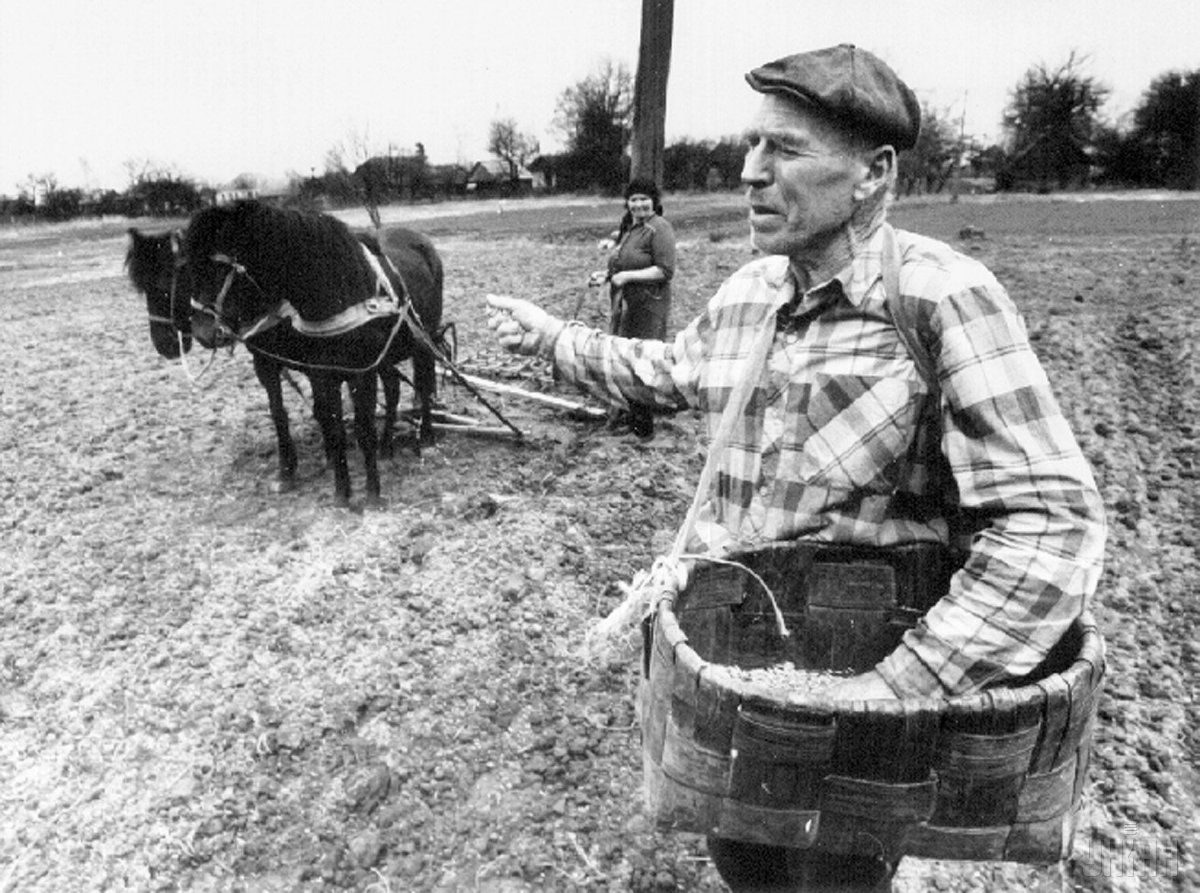
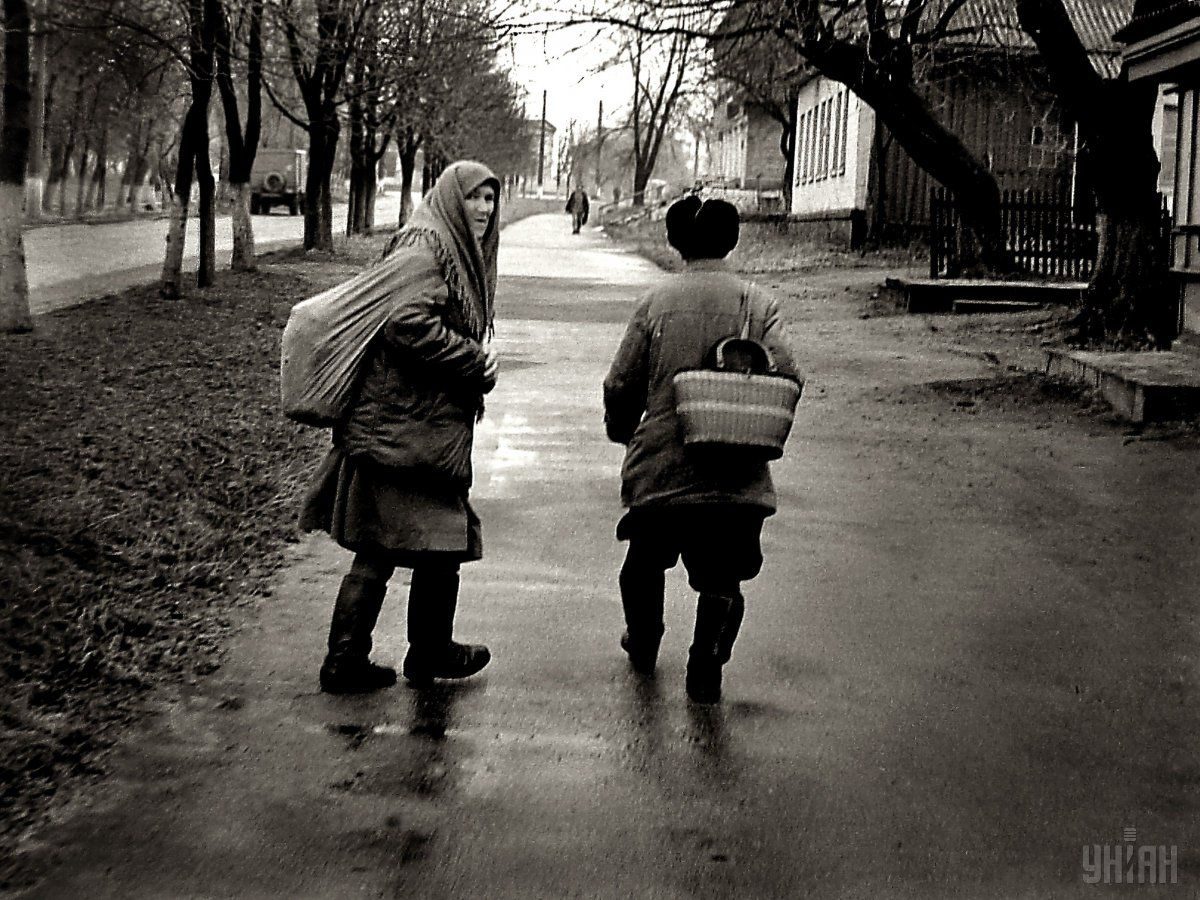
However, despite the contamination of the area and the ban on residence in the Chornobyl zone, some people return to their homes, someone just settled in vacant houses, and some people have not left their homes ever since the disaster.